Prerequisites
- GCC compiler
- For Windows, you will need to install
mingw - For Linux, you will need to refer to your distributions package manager
- For Mac, you will need to use
brew
- For Windows, you will need to install
Compiling C++ Using Terminal
First, let's make a simple C++ file named
main.cpp// main.cpp #include <iostream> int main() { std::cout << "Hello World!\n"; }Now, open your terminal in the same directory where the file was saved.
To compile the file
$ g++ main.cppYou can replace
main.cppwith the filename you chose. This will compile your file into an executable calleda.out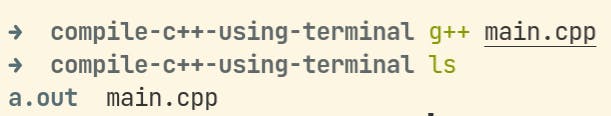
Finally, to run the file
$ ./a.out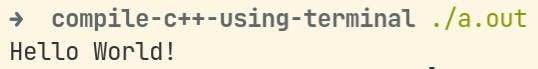
Incase you want to name the executable file
$ g++ main.cpp -o mainThis will make the executable file as
main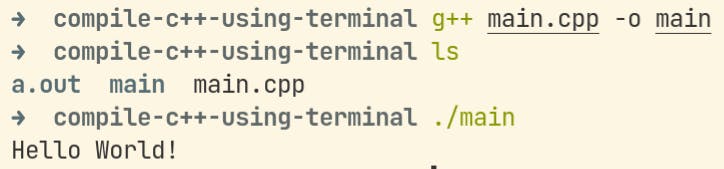
Compiling C++ Files with Header Files
You've divided your main file into multiple files. Now what?
I created a new file called
Universe.hppinincludesdirectory andmain.cppintosrcdirectory My directory now looks like. ├── includes │ └── Universe.hpp └── src └── main.cpp// Universe.hpp #pragma once #include <iostream> class Universe { public: Universe() { std::cout << "Hello Universe\n"; } };and I changed my
main.cppto// main.cpp #include <iostream> #include "Universe.hpp" int main() { std::cout << "Hello World!\n"; Universe universe; }If I compile my main file now, I get an error

What this means is that gcc can't find my
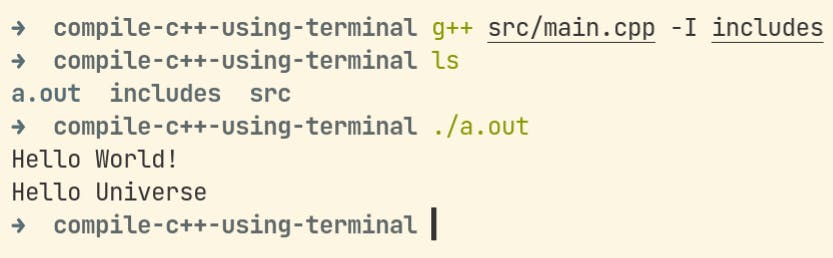
Universe.hppfile, we need to tell where the file is.To tell gcc where are header files are located, we will use
-Iflag$ g++ src/main.cpp -I includesIt compiles just fine with no errors and runs as well!
Conclusion
g++is used to compile C++ on terminal-oflag is used to name output executable-Iis used to include header files directory